Abstract
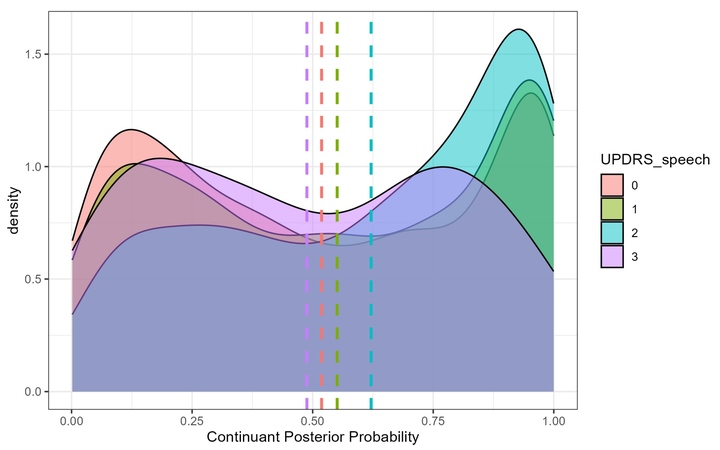
Background/Objectives: Parkinson’s disease (PD) affects both articulatory and phonatory subsystems, leading to characteristic speech changes known as hypokinetic dysarthria. However, few studies have jointly analyzed these subsystems within the same participants using interpretable deep-learning-based measures. Methods: Speech data from the PC-GITA corpus, including 50 Colombian Spanish speakers with PD and 50 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were analyzed. We combined phonological feature posteriors—probabilistic indices of articulatory constriction derived from the Phonet deep neural network—with harmonics-to-noise ratio (HNR) as a laryngeal measure. Linear mixed-effects models tested how these measures related to disease severity (UPDRS, UPDRS-speech, and Hoehn and Yahr), age, and sex. Results: PD participants showed significantly higher [continuant] posteriors, especially for dental stops, reflecting increased spirantization and articulatory weakening. In contrast, [sonorant] posteriors did not differ from controls, indicating reduced oral constriction without a shift toward more open, approximant-like articulations. HNR was predicted by vowel height and sex but did not distinguish PD from controls, likely reflecting ON-medication recordings. Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that deep-learning-derived articulatory features can capture early, subphonemic weakening in PD speech—particularly for coronal consonants—while single-parameter laryngeal indices such as HNR are less sensitive under medicated conditions. By linking spectral energy patterns to interpretable phonological categories, this approach provides a transparent framework for detecting subtle articulatory deficits and developing feature-level biomarkers of PD progression.